Steam Jacketed Valves: Structure, Function and Applications
Steam jacketed valves are specialized valves designed to provide excellent thermal insulation and cold preservation properties. These valves not only minimize heat loss in pipeline media but also ensure that the medium remains at the optimal temperature for flow, whether in high or low-temperature environments. Steam jacketed valves are essential for handling high-viscosity or easily crystallized and solidified media, making them indispensable in industries such as petroleum, chemical, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals. This article explores the structure, function, applications, and differences between steam jacketed valves and standard valves, offering a comprehensive understanding of their unique benefits.
Structure and Working Principle of Steam Jacketed Valves
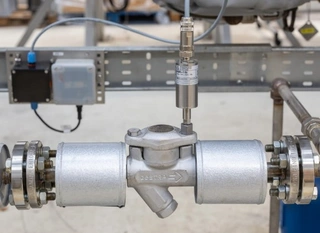
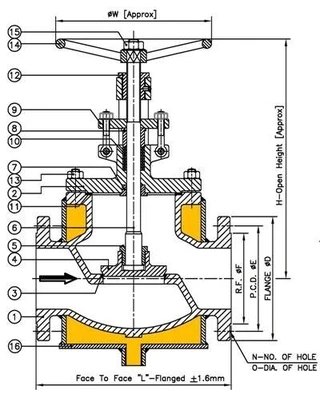
The key feature of steam jacketed valves is the metal jacket welded around the exterior of the valve body. This jacket is equipped with inlet and outlet ports, allowing the injection of various thermal media such as steam, thermal oil, cooling water, or cold air. These media regulate the temperature of the process medium inside the valve body, achieving insulation or cold preservation.
The metal jacket is designed to maintain the medium's temperature within the desired range by either heating or cooling the process fluid. This temperature control prevents the medium from condensing, crystallizing, or becoming overly viscous, ensuring smooth and efficient valve operation. The structural design of steam jacketed valves is especially beneficial for preventing high-viscosity media from solidifying or crystallizing at low temperatures, ensuring the uninterrupted operation of the pipeline system.
Additionally, the valve's diameter typically matches the pipeline diameter, optimizing fluid transmission and minimizing heat loss. The insulation provided by the jacket not only protects the medium and the pipeline but also enhances the system's overall energy efficiency, reducing unnecessary consumption.

Functions of Steam Jacketed Valves
Steam jacketed valves perform several critical functions in pipeline systems, particularly when dealing with media that tend to solidify, crystallize, or change viscosity at room temperature. The main functions of steam jacketed valves include:
1. Reducing Heat Loss
Steam jacketed valves are designed to minimize heat loss in pipeline media, especially when transporting temperature-sensitive substances. The thermal medium flowing through the jacket prevents heat from escaping, ensuring that the medium remains within the appropriate temperature range throughout its journey in the pipeline.
2. Preventing Crystallization and Solidification
For high-viscosity or easily crystallized substances like asphalt, resin, or glue, traditional valves can cause blockages or crystallization, which may obstruct flow or damage the valve seals. Steam jacketed valves, by regulating temperature, prevent these issues, ensuring the medium flows smoothly and efficiently through the system.
3. Ensuring Normal Valve Operation
The design of steam jacketed valves ensures that they can open and close effectively under extreme temperature conditions. The insulation or cold preservation provided by the jacket prevents the medium from freezing or adhering to the valve body, which helps maintain proper sealing and reliable operation.
Application Areas of Steam Jacketed Valves
Steam jacketed valves are widely utilized across industries where the transportation of high-viscosity, easily crystallized, or high/low-temperature media is required. Some typical applications are as follows.
1.Petroleum Industry
In asphalt transport systems, steam jacketed valves are essential for preventing substances like asphalt from solidifying in the pipeline. Large-diameter, high-pressure, high-sealing performance steam jacketed ball valves are commonly used to ensure the medium remains fluid and the system operates efficiently.
2. Chemical Industry
Many chemicals, such as resins and glues, need to be kept at specific temperatures to maintain fluidity during processing. Steam jacketed valves prevent clogging of the pipeline due to the condensation of high-viscosity substances, thus enhancing production efficiency and safety.
3. Food Industry
Steam jacketed valves are crucial in the food production process to prevent spoilage or contamination due to temperature fluctuations. For example, they help maintain temperature stability during the production of liquid foods or chemical additives, ensuring that products remain safe and of high quality.
4. Metallurgy and Pharmaceutical Industries
These industries frequently transport high-temperature or low-temperature fluids. Steam jacketed valves maintain the required temperature for such fluids, ensuring that their physical and chemical properties remain intact, thus preventing quality degradation due to temperature variations.
Differences Between Steam Jacketed Valves and Standard Valves
The primary distinction between steam jacketed valves and standard valves lies in their structure and functionality. Standard valves are generally simpler, with a flange connecting them to the pipeline, but they lack any mechanism for temperature regulation. In contrast, steam jacketed valves feature a metal jacket surrounding the valve body, with ports for injecting steam, thermal oil, or other temperature-regulating media. Key differences include:
1. Temperature Control Function
Steam jacketed valves can regulate the temperature of the medium inside the valve body by injecting thermal media, thus preventing solidification or crystallization at low temperatures or overheating at high temperatures. Standard valves do not have this capability and cannot control the temperature of the medium.
2. Structural Design
Steam jacketed valves have a metal jacket welded to the valve body, enabling the injection of thermal media to maintain a constant temperature. Standard valves, however, only consist of a basic valve body and lack any insulation or temperature control features.
3. Applicable Media
Steam jacketed valves are suitable for handling high-viscosity, easily crystallized, or solidified media, such as asphalt, resin, and glue. Standard valves are more appropriate for conventional media with good fluidity and do not require temperature control.
Conclusion
Steam jacketed valves are specifically designed to handle high-viscosity, easily crystallized, or solidified media. By incorporating a metal jacket around the valve body and injecting thermal media such as steam or thermal oil, they regulate the temperature of the medium inside the valve body, providing insulation or cold preservation. These valves effectively reduce heat loss, prevent medium condensation or clogging, and ensure smooth flow under varying temperature conditions. Widely used in industries such as petroleum, chemical, food, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals, steam jacketed valves play a key role in improving production efficiency, ensuring product quality, and safeguarding the integrity of complex pipeline systems.
Send your message to this supplier
Related Articles from the Supplier
What are Inverted Bucket Steam Traps?
- Aug 29, 2025
Maintenance Guide for Steam Trap Failures
- Oct 24, 2025
How to Properly Install Steam Traps: Complete Guide
- Dec 24, 2025
What is Bimetallic Steam Trap?
- Dec 26, 2025
What Is a Thermodynamic Steam Trap
- Jan 22, 2026
Related Articles from China Manufacturers
Steam Jacketed Globe Valves: Basics and Applications
- Feb 27, 2024
Design Improvement of Steam Jacketed Ball Valves
- Nov 16, 2024
You Need to Know About Steam Jacketed Globe Valves
- Feb 28, 2024
Steam Jacketed Ball Valve: Design and Applications
- Oct 25, 2024
Steam Valves Information
- Mar 05, 2019
Related Products Mentioned in the Article
Zhejiang Kosen Valve Co., Ltd.
- https://www.kosenvalve.com/
- Business Type: Industry & Trading, Manufacturer,
Supplier Website
Source: https://www.kosenvalve.com/media-hub/steam-jacketed-valves-structure-function-and-applications.html