What Is a Thermodynamic Steam Trap
In industrial production, steam systems are an indispensable part of many plants. Steam is not only used for heating and driving mechanical equipment, but also plays a critical role in numerous process operations. However, during operation, steam systems inevitably generate condensate. If this condensate is not discharged in a timely manner, it can reduce equipment efficiency and even cause damage. Therefore, steam traps are key components that ensure the efficient operation of steam systems. Today, we take an in-depth look at a highly efficient and widely used type of steam trap, the thermodynamic steam trap.
Basics of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
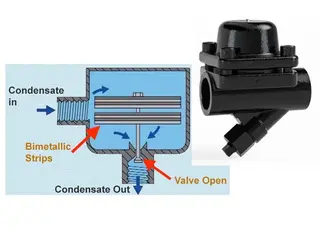
A thermodynamic steam trap is a steam trap with a simple structure and reliable operation. Its main component is a flat, disc-shaped metal cap that controls the flow of condensate and steam based on thermodynamic and dynamic principles.
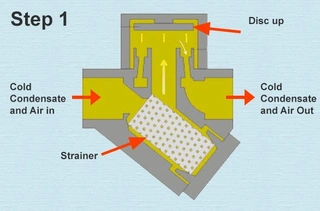
1. Basic Structure of a Thermodynamic Steam Trap
The core component of a thermodynamic steam trap is a metal cap, commonly referred to as a disc. This disc is the only moving part and rests on a flat control seat. The valve body is typically made of stainless steel, a material that offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
A small projection is provided on the top of the valve cover to prevent the disc from being drawn upward and sticking, ensuring that the disc can move freely up and down. This design guarantees reliable opening and closing of the valve.
2. Working Principle of a Thermodynamic Steam Trap
The operating principle of a thermodynamic steam trap is based on the physical characteristics of steam and condensate. When condensate enters the trap passage, the disc remains open, allowing the condensate to be discharged smoothly. As steam enters the passage and replaces the condensate, the pressure above and below the disc gradually equalizes.
Because the effective area above the disc is larger than that below it, the downward force acting on the disc becomes greater, causing the disc to move downward and close the passage.
Once the disc seals tightly, steam is trapped within the passage. When additional condensate enters, the trapped steam cools and condenses, reducing the pressure above the disc. When the pressure drops to a certain level, the disc lifts again, allowing condensate to be discharged. This cycle repeats continuously, ensuring timely condensate removal while preventing steam loss.
Types of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Thermodynamic steam traps are available in several types, each with its own characteristics and application scenarios. Common types include the following:
1. Disc-Type Steam Traps
Disc-type steam traps are the most common form of thermodynamic steam traps. They operate on the same principle but feature an additional outer cap. The inner chamber of the cap is connected to the steam pipeline, using pipeline steam to insulate the main steam chamber of the trap.
This design helps maintain the temperature and pressure in the main chamber, ensuring tight closure of the trap. When condensate forms in the pipeline, the outer cap cools, and the trap begins to discharge condensate. Disc-type steam traps are especially suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, and superheated steam applications, offering high efficiency and durability.
2. Impulse Steam Traps
Impulse steam traps regulate valve opening and closing through two orifice plates based on changes in steam pressure drop. Even when the valve is fully closed, the inlet and outlet remain connected through two small orifices, so the trap is never completely shut.
As a result, steam continuously escapes, leading to relatively high steam loss. Impulse steam traps operate at a very high frequency, which causes significant wear and a shorter service life. Nevertheless, they are compact, resistant to water hammer, capable of discharging air and saturated-temperature condensate, and provide near-continuous drainage, making them suitable for specific industrial applications.
3. Orifice Plate Steam Traps
Orifice plate steam traps control condensate discharge by selecting orifice plates with different diameters. Their structure is simple, but improper selection may result in insufficient drainage or excessive steam loss.
Therefore, they are not suitable for intermittently operated steam equipment or applications with large fluctuations in condensate load. Accurate calculation based on actual condensate flow requirements is essential to ensure efficient operation.
Advantages of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Thanks to their unique design and operating principle, thermodynamic steam traps offer several significant advantages that make them popular in industrial applications.
- Simple structure and easy maintenance: Thermodynamic steam traps have an extremely simple structure with only one moving part, the disc. This simplicity reduces manufacturing costs and minimizes the likelihood of failure. Maintenance is very convenient, as the disc can often be inspected or replaced without removing the trap from the pipeline, significantly reducing downtime and improving productivity.
- High-pressure and high-temperature resistance: Typically made of stainless steel, thermodynamic steam traps provide excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance. They can operate reliably in high-pressure steam systems and high-temperature superheated steam environments, ensuring stable and efficient system operation.
- Resistance to water hammer and vibration: Water hammer is a common issue in steam systems and can cause severe equipment damage. The compact and robust design of thermodynamic steam traps enables them to withstand water hammer and vibration, maintaining stable operation even under harsh conditions and extending service life.
- No adjustment or internal modification required: Thermodynamic steam traps are designed to automatically adapt to varying operating conditions without the need for adjustments or internal component changes. This self-regulating capability reduces maintenance workload and enhances reliability and stability.
Limitations of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Despite their many advantages, thermodynamic steam traps also have certain limitations. Understanding these limitations helps ensure proper selection and application.
- Not suitable for low differential pressure applications: Thermodynamic steam traps cannot operate properly under low differential pressure conditions. When the pressure difference is too low, the flow velocity beneath the disc is insufficient to generate the low pressure required for disc movement. Generally, the inlet pressure should not be lower than 0.25 MPa, and the back pressure should not exceed 80% of the inlet pressure.
- Some degree of steam loss: Because the operating force of thermodynamic steam traps is derived from steam, a small amount of steam loss is unavoidable during operation. While this loss is relatively minor, it may be a concern in applications with extremely high energy-efficiency requirements.
- Noise issues: Thermodynamic steam traps can generate noise during operation. In noise-sensitive environments such as hospital wards or operating rooms, this may be disruptive. However, installing a silencer can effectively reduce noise levels and broaden their range of applications.
Application Scenarios of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Due to their efficiency, reliability, and durability, thermodynamic steam traps are widely used across various industries. Common applications include:
- Steam pipeline systems: They are used to discharge condensate from steam pipelines, ensuring smooth steam flow. By rapidly removing condensate while preventing steam leakage, they significantly improve system efficiency and reduce energy waste.
- Heating equipment: In heating equipment such as steam boilers and heat exchangers, thermodynamic steam traps promptly discharge condensate, maintaining high heat transfer efficiency, improving productivity, and reducing equipment wear.
- High-pressure and superheated steam environments: Thermodynamic steam traps are particularly suitable for high-pressure and superheated steam systems. Their ability to withstand extreme pressure and temperature conditions ensures safe and efficient operation in such environments.
Installation and Maintenance of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure efficient operation.
1. Installation Guidelines
- Horizontal installation: Thermodynamic steam traps must be installed horizontally to allow free movement of the disc. Improper installation may cause the disc to stick or malfunction.
- Low-point installation: The trap should be installed at the lowest point near the condensate outlet of the equipment to ensure smooth condensate flow and efficient drainage.
- Correct piping connections: Ensure correct pipe connections and matching pipe diameters to prevent leakage and ensure smooth condensate discharge.
2. Maintenance Guidelines
- Regular inspection: Periodically check the operating condition of the trap. The characteristic “clicking” sound during opening and closing can indicate normal operation. Abnormal sounds may signal disc wear or sticking.
- Cleaning and upkeep: Regularly clean the trap, especially the sealing surfaces and disc, to prevent debris accumulation that can affect sealing and service life.
- Component replacement: If severe disc wear or sealing surface damage is found, replace the components promptly, ensuring that replacement parts match the original specifications.
Selection and Installation Considerations of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Correct selection and installation are critical for optimal performance.
1. Selection Considerations
- Select according to actual requirements: Choose a trap based on actual condensate load and steam pressure. Oversizing may cause excessive disc cycling and wear, while undersizing may result in inadequate drainage.
- Consider the operating environment: High-pressure and high-temperature environments require traps with appropriate resistance, while corrosive environments demand corrosion-resistant materials.
- Consider maintenance costs: Select traps that are easy to maintain and have low replacement part costs to reduce long-term operating expenses.
2. Installation Considerations
- Ensure correct installation direction: Thermodynamic steam traps have a specified flow direction. Incorrect installation may prevent proper operation.
- Install a condensate collection pocket: For main line drainage, use a low-capacity trap and properly install a condensate collection pocket to ensure efficient drainage.
- Avoid vertical installation: When the disc is oriented vertically and discharges directly to atmosphere, disc edge wear increases. Vertical installation should be avoided whenever possible.
Conclusion
Thermodynamic steam traps are efficient, reliable, and durable devices widely used in industrial steam systems. Through a simple structure and a unique thermodynamic operating principle, they ensure rapid condensate discharge and effective steam sealing.
Although they are unsuitable for low differential pressure applications and may involve minor steam loss and noise, proper selection and installation can maximize their advantages and mitigate these limitations.
In practical applications, selecting the appropriate thermodynamic steam trap based on operating conditions and strictly following installation and maintenance requirements is essential. By doing so, steam system efficiency can be improved, energy consumption reduced, and operating costs lowered. With their excellent performance and broad applicability, thermodynamic steam traps have become an indispensable component of industrial steam systems.
Send your message to this supplier
Related Articles from the Supplier
What Is a Thermodynamic Steam Trap
- Jan 22, 2026
What is a Duplex Spring Safety Valve?
- Sep 17, 2025
What is Explosion-Proof Electric Ball Valve
- Dec 22, 2025
What is Bimetallic Steam Trap?
- Dec 26, 2025
What is Dual Plate Wafer Check Valve
- Jan 05, 2026
What is Double Eccentric Segmented Ball Valve
- Jan 13, 2026
Related Articles from China Manufacturers
What Is a Dynamic Load Balancing EV Charger?
- Sep 06, 2024
What is a Pneumatic Actuator and how does it Work?
- Jun 17, 2020
What is a Water Hammer
- Jul 13, 2020
What is a Knife Gate Valve?
- Aug 27, 2020
What is A Motorcycle Disc Brake Lock
- May 11, 2015
What Is a Disc Brake Lock?
- Oct 25, 2023
What Is a Motorcycle Saddlebag Lock?
- Nov 17, 2023
What Is a Passive Cam Lock?
- Dec 21, 2023
Related Products Mentioned in the Article
Zhejiang Kosen Valve Co., Ltd.
- https://www.kosenvalve.com/
- Business Type: Industry & Trading, Manufacturer,
Supplier Website
Source: https://www.kosenvalve.com/media-hub/what-is-a-thermodynamic-steam-trap.html