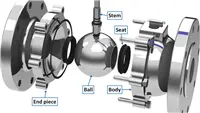
Ball Valve Trim Types: Selection and Application Guide
In industrial pipeline systems, ball valves, as important control components, are widely used in applications such as media shutoff, distribution, and flow regulation. The core components of a ball valve are its internal trims. Different trim types give ball valves different performance characteristics and application scenarios. This article will comprehensively explore common ball valve trim types, including floating ball, trunnion-mounted ball, V-shaped ball, eccentric ball, orbit-type ball, and inclined-seat designs, helping readers better understand and select suitable ball valve trims to meet different engineering requirements.
Floating Ball Valve: A Simple & Practical Sealing Solution
The structure of a floating ball valve is relatively simple. Its core component is a ball with a through-bore equal to the pipeline diameter. The sealing of the ball relies on the pressure of the medium. When the valve is closed, the upstream medium pressure acts on the ball and pushes it tightly against the downstream sealing seat, thereby forming a seal. This sealing method is known as pressure-assisted self-sealing, which does not require additional external force to achieve sealing.
1. Advantages of Floating Ball Valves
- Simple structure: Floating ball valves have a relatively simple structure, are easy to manufacture and maintain, and have relatively low cost.
- Good sealing performance: Within certain diameter and pressure ranges, floating ball valves provide very reliable sealing performance and can effectively prevent media leakage.
- Low flow resistance: Since the ball bore is consistent with the pipeline diameter, the resistance encountered by the medium when passing through the valve is small, which helps improve the overall efficiency of the pipeline system.
- High cost performance: In small- and medium-diameter as well as low- to medium-pressure applications, floating ball valves offer excellent cost performance and are the preferred choice for many projects.
2. Limitations of Floating Ball Valves
- Limited application range: Floating ball valves are not suitable for large-size applications. When the valve diameter is too large or the pressure is too high, the weight of the ball and the media load increase, leading to a decline in sealing performance. In addition, the weight of the ball directly acts on the sealing ring, which may cause irregular deformation of the sealing ring, affecting valve service life and sealing performance.
- Higher operating torque: When the ball is subjected to a large working media load, the friction between the ball and the sealing ring increases, resulting in higher opening and closing torque. This limits the application of floating ball valves under large-diameter or high-pressure conditions to a certain extent.
- Uncertain automatic pressure relief function: Floating ball valves can be designed with single-seat sealing or double-seat sealing. A single-seat floating ball valve can realize automatic pressure relief of the valve cavity, but this function is not a default option for all manufacturers. If a specific pressure relief function is required, it should be clearly specified in the bill of materials or datasheet.
3. Applications of Floating Ball Valves
Floating ball valves are widely used in small- and medium-diameter pipeline systems such as municipal water supply, natural gas transmission, and chemical media transportation. Due to their simple structure, good sealing performance, and low cost, they are very suitable for low- and medium-pressure operating conditions.

Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valve: Complex Structure for High Performance
The core component of a trunnion-mounted ball valve is a fixed ball. The ball establishes sealing contact pressure with the valve core through spring-supported floating seats to achieve shutoff sealing. The floating seat consists of the seat body, sealing ring, support spring, and sealing rings, resulting in a relatively complex structure and larger overall size.
Trunnion-mounted ball valves do not rely on media pressure to achieve sealing. The sealing is reliable and bidirectional sealing is easy to achieve, making them commonly used in large-diameter applications.
1. Advantages of Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valves
- Reliable sealing: Trunnion-mounted ball valves provide very reliable sealing performance and can achieve good sealing even without media pressure, giving them clear advantages in large-diameter and high-pressure applications.
- Bidirectional sealing: Trunnion-mounted ball valves can achieve bidirectional sealing, maintaining good sealing performance in both flow directions. This is especially important for pipeline systems requiring bidirectional sealing.
- Wide application range: Due to their structural characteristics, trunnion-mounted ball valves are suitable for large diameters and high-pressure conditions and can meet the requirements of various complex projects.
- Fire-safe function: Trunnion-mounted ball valves are designed and manufactured in accordance with API 607 and API 6FA standards and feature fire-safe performance. Under extreme conditions such as fire, the grease injection valve can quickly inject sealing grease to mitigate leakage and ensure valve safety.
2. Limitations of Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valves
- Complex structure: Trunnion-mounted ball valves have a complex structure, higher manufacturing costs, and relatively greater maintenance difficulty.
- Automatic pressure relief must be specified: Trunnion-mounted ball valves cannot automatically relieve pressure in a sealed valve cavity. If this function is required, it must be clearly specified in the bill of materials or datasheet.
- Higher operating torque: Similar to floating ball valves, trunnion-mounted ball valves experience increased opening and closing torque in large-diameter or high-pressure conditions due to greater friction between the ball and the sealing ring.
3. Applications of Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valves
Trunnion-mounted ball valves are widely used in large-diameter and high-pressure pipeline systems such as oil and gas transmission, chemical media transportation, and municipal gas systems. Their reliable sealing performance and bidirectional sealing capability make them the preferred choice for many large-scale projects.
V-Port Ball Valve: Special Design for Specific Requirements
A V-port ball valve is a special type of ball valve whose closing element is a hemispherical ball with a V-shaped opening. The V-shaped opening has a sharp cutting edge, and during rotation of the ball, a wiping action occurs between the closing elements, providing strong cutting capability for the medium.
V-port ball valves not only provide on/off functionality but also offer throttling capability, functioning as a quarter-turn control valve. Their sealing performance is the same as that of ordinary ball valves. The flow characteristic is equal percentage, with a turndown ratio of up to 100:1, and they are widely used in industrial process control systems.
1. Advantages of V-Port Ball Valves
- Cost efficiency: Hemispherical ball valves reduce ball weight, thereby lowering manufacturing costs and making them suitable for cost-sensitive applications.
- Excellent control performance: The V-shaped opening and seat flow passage form a fan-shaped area. During rotation, the flow passage cross-sectional area changes, enabling precise regulation of the medium. Among ball valves, V-port ball valves offer the best control performance, with equal-percentage flow characteristics and a high turndown ratio, making them suitable for applications requiring precise flow control.
- Strong adaptability: The shearing action between the V-shaped notch and metal seat makes V-port ball valves particularly suitable for media containing fibers, fine solid particles, slurries, and similar materials. The smooth and rounded internal flow passage prevents media accumulation and is suitable for controlling various complex media.
2. Applications of V-Port Ball Valves
Hemispherical ball valves are mainly used in mining and similar media pipelines, suitable for applications where cost reduction is required and sealing performance requirements are not particularly high.
V-port ball valves are widely used in industrial process control systems, such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries, for precise control of media flow.
Eccentric Ball Valve: Reduced Wear and Extended Service Life
Eccentric ball valves use the sealing principle (cam effect) of eccentric butterfly valves to generate the required sealing contact pressure while reducing or avoiding wear between internal components and the seat.
Compared with trunnion-mounted ball valves, eccentric ball valves rely on stem torque to generate sealing pressure. The triple-offset structure avoids wear between the internal components and the seat, providing better service performance than trunnion-mounted ball valves. However, improper eccentric offset design may instead reduce valve performance.
1. Advantages of Eccentric Ball Valves
- Reduced wear: The triple-offset structure effectively reduces wear between internal components and the seat, extending valve service life.
- Good sealing performance: Eccentric ball valves provide very reliable sealing performance under various operating conditions.
- Easy operation: Eccentric ball valves require relatively low operating torque, enabling smooth opening and closing and suitability for frequent operation.
2. Limitations of Eccentric Ball Valves
- High design requirements: Precise calculation of eccentric offset is required. Improper design can negatively affect valve performance.
- High manufacturing difficulty: Eccentric ball valves involve complex manufacturing processes and require high machining accuracy, resulting in relatively higher cost.
3. Applications of Eccentric Ball Valves
Eccentric ball valves are widely used in applications requiring reduced wear and extended service life, such as chemical, oil, and natural gas industries. Their reliable sealing performance and low operating torque make them a preferred choice in many projects.
Orbit Ball Valve: Combining Gate and Ball Valve Advantages
An orbit ball valve is a new type of ball valve that combines the advantages of gate valves and ball valves. The ball is a composite structure with a wedge-shaped cone in the center and 5° inclined surfaces on both sides. Each side consists of a spherical valve segment with inclined surfaces.
The movement trajectory of the stem is restricted by guide slots. The opening and closing process exhibits both gate valve characteristics (multi-turn motion) and ball valve characteristics (90-degree rotation).
1. Advantages of Orbit Ball Valves
- Excellent sealing performance: No friction occurs between sealing surfaces, resulting in highly reliable sealing and long service life.
- High operating efficiency: Compared with traditional gate valves, orbit ball valves offer much higher operating efficiency. For example, a DN500 orbit ball valve has a stroke of approximately 60 mm, and its operating time is only about one-seventh that of a traditional gate valve.
- Compact structure: Orbit ball valves have a small installation height and compact structure, facilitating pipeline layout. For a DN500 valve, the center height is approximately 950 mm, significantly lower than the 3500 mm of a traditional gate valve.
- Wide applicability: The sealing surfaces of the seats and spherical valve segments can be hardfaced or coated with high-hardness, corrosion-resistant alloy materials, making them suitable for various high-temperature, high-pressure, low-temperature, and corrosive media pipelines.
2. Limitations of Orbit Ball Valves
- High manufacturing cost: The complex structure results in higher manufacturing cost and stringent machining accuracy requirements.
- High design requirements: Multiple factors must be considered during design, such as stem motion trajectory and valve segment positioning, making design more challenging.
3. Applications of Orbit Ball Valves
Orbit ball valves are widely used in applications requiring efficient operation and reliable sealing, such as oil and gas transmission and chemical media transportation. Their compact structure, high operating efficiency, and excellent sealing performance make them particularly suitable for large-diameter and high-pressure pipeline systems.
Selection Recommendations and Considerations
After gaining an in-depth understanding of the structure, performance, advantages, disadvantages, and application scenarios of various ball valve trim types, selection becomes a critical step. Proper selection not only determines whether the valve can operate normally under specific conditions but also affects the safety, stability, and economic operation of the entire pipeline system.
1. Trim Selection by Operating Conditions
Small and medium diameter, low to medium pressure: Floating ball valves are preferred due to their simple structure, good sealing performance, low flow resistance, and high cost performance.
Large diameter, high pressure: Trunnion-mounted ball valves are a better choice due to reliable sealing and excellent bidirectional sealing performance.
Applications requiring flow regulation: V-port ball valves are the best option, offering superior control performance and favorable flow characteristics.
Applications requiring reduced wear and extended service life: Eccentric ball valves are ideal, as their triple-offset structure effectively reduces wear.
Applications requiring efficient operation and compact structure: Orbit ball valves are an innovative choice, combining the advantages of gate valves and ball valves.
2. Clarifying Special Functional Requirements
Automatic pressure relief: If valve cavity automatic pressure relief is required, it should be clearly specified in the bill of materials or datasheet.
Fire-safe performance: For applications requiring fire safety, select ball valves that comply with API 607 and API 6FA standards.
Sealing material selection: Select appropriate sealing materials, such as metal hard seats or PTFE soft seats, based on media properties and operating conditions.
3. Considering Cost and Maintenance
Cost performance: Select ball valve trim types with high cost performance while meeting operating requirements.
Ease of maintenance: Choosing valves with simple structures and easy maintenance can reduce long-term operating costs.
Conclusion
As an important industrial valve, the selection of ball valve trim types has a significant impact on valve performance and service life. Floating ball valves, trunnion-mounted ball valves, hemispherical ball valves, V-port ball valves, eccentric ball valves, orbit ball valves, and inclined-seat ball valves each have their own characteristics and applicable ranges.
When selecting ball valves, comprehensive consideration should be given to specific operating conditions, media properties, operational requirements, and cost factors to choose the most appropriate trim type. Through proper selection, ball valves can deliver optimal performance under various complex conditions, improving the safety and reliability of pipeline systems.
We hope this article is helpful for ball valve selection and application. If you have any questions or require further technical support, please feel free to contact us.
Send your message to this supplier
Related Articles from the Supplier
Ball Valve Leakage: Causes, Prevention and Solutions
- Feb 13, 2026
Pneumatic Ball Valve Selection Guide
- Sep 15, 2025
Installation of welded ball valve
- Dec 14, 2024
An Introduction to Orbit Ball Valve
- Nov 26, 2025
Related Articles from China Manufacturers
Landee Announced New Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
- Jan 16, 2013
Causes and Solutions of Ball Valve Internal Leakage
- Mar 27, 2019
Application of Ball Valve in Aerospace Industry
- Jun 11, 2020
Difference between Ball Valve and Butterfly Valve
- Jun 28, 2020
What is Ball Valve?
- Jul 29, 2015
Related Products Mentioned in the Article
Zhejiang Kosen Valve Co., Ltd.
- https://www.kosenvalve.com/
- Business Type: Industry & Trading, Manufacturer,
Supplier Website
Source: https://www.kosenvalve.com/media-hub/ball-valve-trim-types-selection-and-application-guide.html














.jpg)