An Introduction to Countergravity Casting Technology
In modern manufacturing, casting technology has always been one of the key processes in the production of metal components. From automobile wheels to aircraft engine parts, from simple daily necessities to complex industrial equipment, the applications of casting technology are everywhere. However, traditional casting methods often face many challenges, such as internal defects in castings, insufficient dimensional accuracy, and low production efficiency. Fortunately, with the continuous advancement of technology, an innovative process known as countergravity casting technology has emerged, and it is changing the face of the casting industry.
Definition and Principle of Countergravity Casting Technology
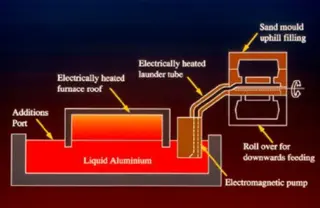
Countergravity casting technology is a unique casting process, the core of which lies in the fact that the driving force of molten metal filling the mold is opposite to the direction of gravity. In other words, during the filling process, the molten metal flows against the direction of gravity. The key to this technology is the application of external driving force. During the process of molten metal filling the mold, the external force plays a dominant role, helping the molten metal overcome its own gravity, cavity resistance, and other external influences, thereby smoothly completing the filling process.
One of the greatest advantages of this process is its controllability. By precisely controlling the magnitude of the external force, operators can achieve different filling speeds to meet various process requirements. For example, when producing thin-walled castings, a lower filling speed is required to avoid turbulence and porosity in the molten metal; while for thick-walled castings, a higher filling speed is needed to ensure that the molten metal fully fills the mold cavity. In addition, countergravity casting technology allows castings to solidify under higher pressure, thereby improving the feeding ability of the molten metal and effectively reducing defects such as shrinkage cavities, porosity, and pinholes.
The principle of countergravity casting can be traced back to Pascal’s Law. Pascal’s Law states that in a closed fluid system, the pressure applied to the fluid is transmitted evenly to all parts of the fluid. In countergravity casting, a pressure difference is established between the mold and the molten metal, enabling the molten metal to fill the mold under the effect of pressure. This pressure difference can be generated in various ways, giving rise to different countergravity casting methods.
Types of Countergravity Casting Technology
According to the method of generating pressure, countergravity casting technology can be divided into the following types.
1. Low-Pressure Casting
Low-pressure casting is a widely applied countergravity casting method. In this process, the mold is usually under atmospheric pressure, while the lower chamber forms a pressure difference by introducing air. Under the effect of this pressure difference, the molten metal is lifted and fills the mold, while solidification is completed during the pressure-holding stage. The advantages of this method lie in relatively simple equipment, easy operation, and simple process control. As long as the pressurization during pressure-holding meets requirements, the casting can achieve good feeding results.
Low-pressure casting is widely used, especially in metal mold casting. Since the mold is under atmospheric pressure, the use of metal molds allows convenient opening, closing, and ejection of castings. Therefore, low-pressure metal casting is widely applied in the production of high-quality castings, such as automobile wheels, cylinder blocks, and cylinder heads. In sand mold low-pressure casting, large and high-quality castings can also be produced.
2. Vacuum Suction Casting
Vacuum suction casting is similar to low-pressure casting, but in vacuum suction casting, the lower chamber remains at atmospheric pressure while the upper chamber forms a pressure difference through vacuum extraction. Under the effect of this pressure difference, the molten metal is lifted and fills the mold. Since the mold is under a vacuum environment, the molten metal has better filling ability, making vacuum suction casting particularly suitable for small thin-walled castings. However, the filling pressure difference is relatively small, and the solidification pressure is also low, so its feeding ability is relatively weak.
3. Differential-Pressure Casting
Differential-pressure casting is a more complex countergravity casting method. In differential-pressure casting, pressure differences can be established in two forms: top exhaust and bottom air intake. Compared with low-pressure casting, differential-pressure casting can not only complete filling and feeding under pressure but also, since the mold is under pressure, better utilize the feeding effect of risers, thereby improving the density of castings. This method is especially suitable for producing large thick-walled castings.
4. Pressure-Regulated Casting
Pressure-regulated casting is a countergravity casting method that combines the advantages of low-pressure casting and differential-pressure casting. In this process, both the upper and lower chambers are evacuated simultaneously. After reaching the specified vacuum level, the lower chamber introduces air to form a pressure difference. Under this pressure difference, the molten metal is lifted and fills the mold. After filling, both chambers are simultaneously pressurized according to the pressure difference at completion, so that the mold is under positive pressure, thereby enhancing the feeding ability of the casting.
The advantage of pressure-regulated casting is that it improves the filling ability of molten metal, making it favorable for forming thin-walled castings, while also achieving feeding under pressure and improving the density of castings. However, this method requires precise control of the pressure difference during pressurization, posing very high demands on the control system.
5. Composite Countergravity Casting
Composite countergravity casting is a process that combines the advantages of multiple countergravity casting methods. It can flexibly select different countergravity casting methods according to process requirements to achieve the best casting results. For example, in producing large complex castings, low-pressure casting can first be used for preliminary filling, followed by differential-pressure casting for feeding, and finally by pressure-regulated casting to complete final solidification. This composite process can fully utilize the advantages of each countergravity casting method, improving both casting quality and production efficiency.
Advantages of Countergravity Casting Technology
Compared with traditional casting methods, countergravity casting technology has many significant advantages.
1. Improved Casting Quality
Countergravity casting technology can significantly improve casting quality. Since the molten metal fills the mold under pressure, the contour of the casting is clearer, and dimensional accuracy is higher. For thin-walled castings, this technology performs particularly well. Under pressure, the molten metal can better fill every corner of the cavity, avoiding the insufficient filling problems common in traditional casting.
In addition, countergravity casting reduces internal defects. During crystallization and solidification under pressure, dendrites deform and break, and the cooling rate increases, producing finer grains. Pressure also enhances feeding ability and suppresses gas precipitation in the molten metal, effectively reducing porosity and micropores. As a result, the mechanical properties of castings are significantly improved, with increased strength and toughness.
2. Reduced Production Costs
Countergravity casting can reduce production costs. Improved casting quality reduces scrap rates, thereby lowering costs. In addition, riser size can be reduced or even eliminated in some cases. This is because during solidification shrinkage, continuous feeding can be supplied from the inner gating system. At the same time, the squeezing and plastic deformation effect of pressure strengthens riser feeding. As a result, the amount of metal material required is reduced, further lowering production costs.
3. Increased Production Efficiency
Countergravity casting also improves production efficiency. Since molten metal fills the mold under pressure, the filling speed can be accurately controlled by computer. This means a more stable production process, reducing accidents caused by unstable filling speed. Furthermore, countergravity casting allows automated production, further improving efficiency.
Applications of Countergravity Casting Technology
Countergravity casting technology is widely applied in various industries, especially in automobile manufacturing and aerospace.
In automobile manufacturing, it is extensively used to produce key components such as wheels, cylinder blocks, and cylinder heads. The quality and performance of these parts are directly related to vehicle safety and reliability. By applying countergravity casting, high-quality, high-performance components can be produced to meet the strict requirements of the automotive industry.
In aerospace, countergravity casting also plays an important role. Aerospace components typically require high strength, low weight, and high precision. This technology can meet these requirements, producing high-quality aerospace components. For example, key parts such as engine blades and wings can be manufactured using countergravity casting.
In addition to automotive and aerospace, countergravity casting technology is also widely used in machinery manufacturing, electronic equipment, and medical devices. In machinery manufacturing, it is used to produce various parts such as gears and crankshafts. In electronics, it is used to produce housings, heat sinks, and other components. In medical equipment, it is applied in producing parts such as surgical instruments and artificial joints.
Challenges and Countermeasures of Countergravity Casting Technology
Despite its many advantages, countergravity casting technology also faces challenges in practical application, such as high equipment costs, complex operation, and demanding control system requirements. To address these challenges, the following strategies can be adopted:
1. Reducing Equipment Costs
Through technological innovation and optimized design, reduce the cost of countergravity casting equipment. For example, using new materials and structural designs can reduce manufacturing costs. At the same time, improving equipment reliability and service life can lower maintenance costs.
2. Simplifying Operation Processes
By introducing intelligent control systems and automated equipment, simplify the operation of countergravity casting. For example, developing user-friendly interfaces and automated programs can make operations easier. At the same time, strengthening operator training can improve skill levels and reduce errors.
3. Improving Control System Performance
By developing high-performance control systems, improve the accuracy and stability of countergravity casting. For example, adopting advanced sensor technology and control algorithms can achieve precise process control. Enhancing system reliability and anti-interference capability can further improve stability.
Conclusion
As an innovative casting process, countergravity casting technology is transforming the traditional casting industry. By utilizing external driving force to make molten metal fill molds under pressure, it overcomes many shortcomings of traditional methods, improves casting quality, reduces production costs, and increases efficiency. In future development, countergravity casting will move toward intelligence, automation, environmental protection, high-performance materials, and multidisciplinary integration. Although some challenges remain, through innovation and optimized design, these issues can be solved. We believe countergravity casting technology will play an increasingly important role in the future of manufacturing and make greater contributions to the development of human society.
Send your message to this supplier
Related Articles from the Supplier
Related Articles from China Manufacturers
An Introduction to 2-Axis Take-out Robots
- May 05, 2019
An Introduction to Traverse Take-out Robots
- Feb 15, 2019
An Introduction to a Belt Conveyor
- Jun 26, 2020
An Introduction to Spring Return Lever Ball Valves
- Feb 24, 2025
An Introduction to Cam Locks
- Jul 12, 2019
Related Products Mentioned in the Article
Supplier Website
Source: https://www.forging-casting-stamping.com/an-introduction-to-countergravity-casting-technology.html